Making well-informed decisions and navigating complexities is paramount for companies seeking sustainable growth and success. This is where the discipline of business analysis (BA) emerges as a game-changer. The business analysis is a guiding compass, providing organizations with the critical insights, comprehensive understanding, and strategic direction necessary to drive successful projects and initiatives.
From launching innovative products to optimizing operational efficiency and embracing transformative technologies, business analysis is pivotal in various aspects of an organization’s journey. As organizations strive to remain competitive and adapt to rapidly changing market demands, they recognize the imperative of making data-driven decisions that align with their strategic objectives. This is precisely where the unique skill set of a business analyst becomes indispensable.
Today we will explain more about business analysis and its transformative power. We explore the multifaceted role of business analysts in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) and beyond. From the precise elicitation of project requirements to efficient resource allocation and risk management, we uncover how business analysis empowers companies to stay ahead of the curve and thrive in a fast-paced and competitive environment. Moreover, we shed light on the essential skills and software business analysis techniques that distinguish a proficient business analyst, from analytical prowess to effective communication and domain-specific expertise.
First things first. Let’s focus on every detail step by step.
Importance of BA in Software Development
First, we must explain what a business analyst is and answer the popular question like “what does a business analyst do in software development?”
A BA is a specialist who engages in crucial negotiations with clients, aiming to comprehensively understand the project’s intricacies. Their primary goal is to communicate effectively with the client, extract essential project details, and create innovative solutions catering to the client’s needs. These solutions are then meticulously documented in the Software Requirements Specification (SRS) document, handed over to the design and development teams.
Within the IT sector, business analysts undertake comprehensive analyses of various elements, from initial input information and requirements to the latest trends and existing solutions specific to the task at hand. Their scope of activity encompasses analyzing and identifying potential bottlenecks in the project, diligently seeking optimal solutions, and assessing the effectiveness of these proposed remedies. In essence, business analysts delve into a thorough analysis of everything and everyone associated with the project.
Business analysis is the process that takes place after you find a software development company. And to find the appropriate development team, we recommend you write a software development RFP (request for proposal). To learn more about RFP, follow the hyperlink above.
Let’s proceed to the main benefits of having a business analyst when you build a web or mobile app:
Accurate Requirements Elicitation
Business analysts gather detailed requirements for software development, encompassing both functional and non-functional aspects. They ensure that the software aligns with end-users’ tasks and business needs, resulting in a comprehensive set of behavioral and quality attributes.
Enhanced Effort Estimation
Engaging professionals in business analysis enables accurate effort estimation for software development. Analysts can gauge the resources needed by assessing all requirements and drafting project plans and budgets early in the development life cycle.
Cost Reduction
Though business analysis incurs upfront costs, it ultimately reduces costs. Precise specifications help developers avoid unexpected challenges and additional requirements, streamlining the development process and minimizing unforeseen expenses.
Reliable and Expedited Development
Well-documented requirements allow all participants in the development process to know their roles and expected outcomes. This clarity accelerates development, reducing the likelihood of unforeseen obstacles.
Satisfying Stakeholder Expectations
Stakeholders receive a product that precisely meets their needs and expectations. Business analysts thoroughly consider all nuances, ensuring stakeholders get the desired functionality, leading to customer satisfaction.
By leveraging the expertise of business analysts, software development projects benefit from streamlined processes, reduced costs, and enhanced success rates, ultimately delivering high-quality solutions that align with the client’s vision and end-users’ requirements.
What Is The Role Of Business Analyst In Software Development Life Cycle?
The role of a business analyst in the Software Development Life Cycle is multifaceted and critical to the project’s success. Throughout each phase of the SDLC, the BA collaborates with stakeholders, development teams, and other key players to ensure that the software solution meets the business needs effectively. Here’s a breakdown of the BA’s role in each phase:
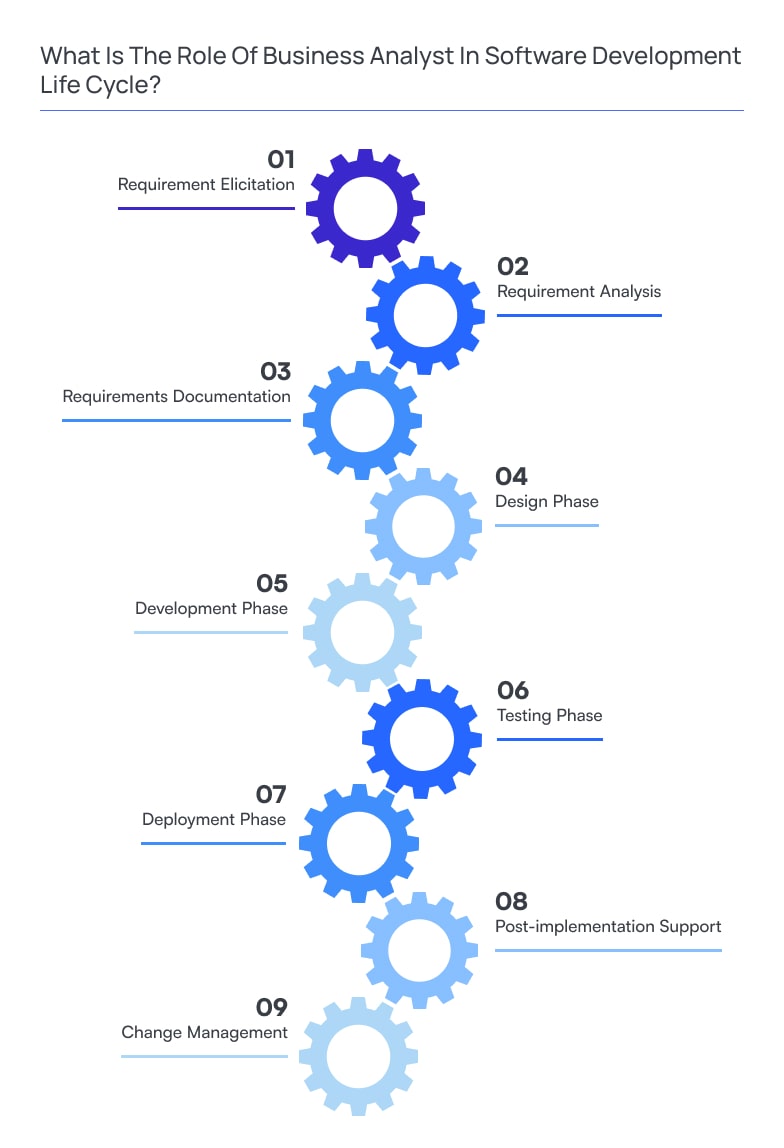
Requirement Elicitation
At the beginning of the SDLC, the BA conducts thorough discussions with stakeholders to gather and understand their requirements. They use interviews, workshops, and surveys to elicit comprehensive and precise requirements.
Requirement Analysis
Once the requirements are gathered, the BA analyzes and prioritizes them, ensuring they are complete, consistent, and feasible. They work closely with stakeholders to resolve conflicts and ambiguities, refining the requirements for further development.
Requirements Documentation
The next business analyst role in software development includes documenting the gathered requirements in a structured manner using tools like use cases, user stories, or functional specifications. This documentation serves as a reference for the development team and ensures everyone involved is on the same page.
Design Phase
During the design phase, the BA works with the development team to explain the requirements and the intended functionalities. They assist in creating technical specifications, ensuring the design aligns with the business needs.
Development Phase
The BA remains engaged with the development team, answering their questions and providing clarifications. They act as the critical point of contact between the business stakeholders and the development team, ensuring that the development process stays focused on meeting the business objectives.
Testing Phase
In the testing phase, the business analyst assists in defining test scenarios and validating the software against the documented requirements. They collaborate with QA teams to ensure the software meets the specified criteria and accurately addresses business needs.
Deployment Phase
The BA plays a role in coordinating the deployment process, ensuring that the software is rolled out smoothly and meets user expectations. They might also assist in user training and support.
Post-implementation Support
After the software is deployed, the BA may continue to support end-users and address any issues or changes that arise. They may also monitor the system’s performance and collect feedback for future enhancements.
Change Management
Throughout the SDLC, the BA helps manage changes due to evolving business needs or external factors. They assess the impact of changes, update documentation, and ensure that the project remains aligned with the business goals.
Overall, business analysts are the bridge between software development’s business and technical sides. Their expertise in understanding and translating business requirements into actionable technical solutions is vital for delivering successful projects that meet the organization’s and its stakeholders’ needs.
Skills A Business Analyst Must Have
Business analysis in software engineering requires a specialist to have diverse skills to excel in their role effectively. These skills can be categorized into technical, analytical, interpersonal, and domain-specific competencies. A business analyst needs some essential skills:
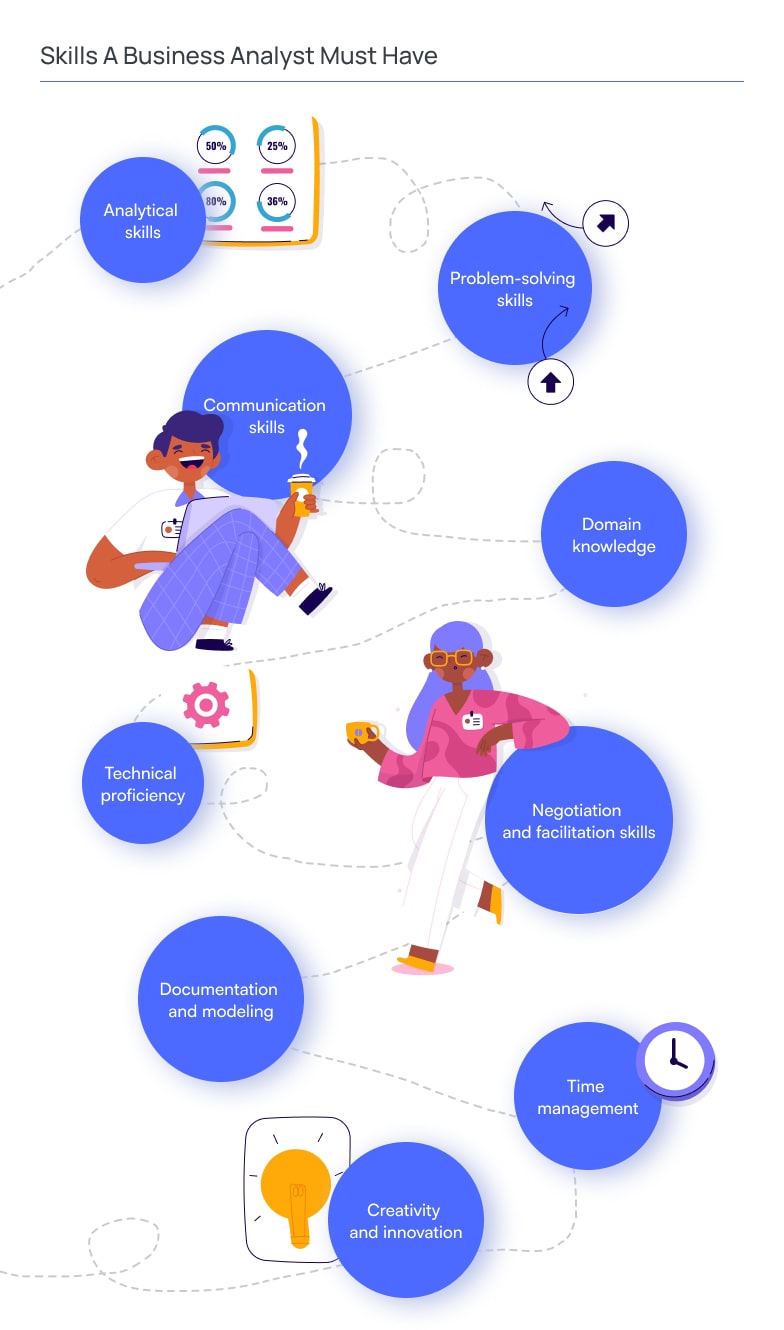
Analytical skills
BAs must possess strong analytical abilities to assess complex problems, gather information, and identify solutions. They should be adept at data analysis, process modeling, and conducting feasibility studies.
Communication skills
Effective communication is crucial for BAs to interact with stakeholders, understand their needs, and convey technical concepts to non-technical individuals. Excellent written and verbal communication skills are essential.
Problem-solving skills
Business Analysts need to be skilled problem solvers, capable of identifying issues, analyzing root causes, and proposing viable solutions that align with business objectives.
Domain knowledge
Understanding the domain or industry in which they work is essential for BAs to comprehend business processes, regulations, and specific terminology related to their projects.
Technical proficiency
While not always required to code, BAs should have a good understanding of technical concepts, IT systems, and software development methodologies to collaborate effectively with developers and other technical team members.
Documentation and modeling
BAs should be proficient in creating clear and structured documentation, such as user stories, use cases, flowcharts, and data models, to effectively communicate requirements to stakeholders and development teams.
Negotiation and facilitation skills
BAs often need to mediate between conflicting stakeholders and facilitate discussions to reach a consensus on project requirements and priorities.
Time management
Managing multiple tasks and deadlines is typical for BAs. Strong time management skills are necessary to prioritize activities and ensure projects progress smoothly.
Creativity and innovation
BAs must think creatively to propose innovative solutions that enhance business processes and add value to projects.
Finally, skills like critical thinking, attention to detail, and adaptability are essential for BAs regardless of their specific domain or industry.
Combining these diverse skills allows business analysts to excel in understanding business needs, bridging the gap between stakeholders and technical teams, and delivering successful projects that fulfill the requirements and objectives of the organization.
Don't miss out on the competitive advantage offered by business analysis. Contact Binerals to discuss how our tailored solutions can help your projects succeed.
Contact BineralsIT Business Analysis Techniques: What BAs Usually Use
Business analysts utilize various techniques and tools to facilitate practical IT business analysis, streamline processes, and make informed decisions. Here are some commonly used techniques and tools in IT business analysis:
SWOT Analysis
SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis is used to evaluate the internal strengths and weaknesses of an organization and the external opportunities and threats it faces. This analysis helps in strategic planning and decision-making.
Workshops
Our interactive workshops facilitate effective stakeholder engagement, fostering collaboration and knowledge exchange. By bringing stakeholders together, we build an analysis plan, identify solutions, manage changes, and establish project priorities. These workshops serve as a platform to elicit valuable insights, uncover hidden challenges, assess business analysis performance, and spark innovative ideas.
Brainstorming
At the core of our analysts’ toolkit is brainstorming, a powerful technique for generating diverse and creative ideas. During brainstorming sessions, stakeholders freely share their thoughts, allowing us to capture a wide range of potential ideas and requirements for the future product. These valuable inputs enrich the business analysis process, ensuring a comprehensive exploration of possibilities.
Stakeholder Analysis
This technique helps identify and analyze stakeholders’ interests, expectations, and influence on the project. It provides effective communication and engagement with key stakeholders.
Data Gathering Techniques
Business analysts use various methods to gather information, including interviews, surveys, workshops, and focus groups, to understand user needs and project requirements.
Data Modeling
Data modeling techniques like Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERD) and Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) help understand data structures and relationships within a system.
Use Case Modeling
Use case diagrams illustrate how users interact with a system and the steps involved in achieving specific tasks, aiding in understanding functional requirements.
Process Modeling
Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) is used to visualize and document business processes, providing insights into process efficiency and identifying areas for improvement.
Decision Matrix
This tool assists in evaluating various options by comparing multiple criteria to make data-driven decisions.
Mind Mapping
To manage information effectively, our analysts create mind maps that visually organize and categorize critical elements. Mind maps serve as dynamic diagrams, capturing tasks, ideas, images, and other relevant details related to the project’s main subject. Utilizing mind mapping, our business analysts gain deeper insights into the project, enabling them to elicit and document detailed requirements accurately.
Requirements Management Tools
These tools help manage and document requirements throughout the project life cycle, ensuring traceability and change management.
Agile Tools
Agile project management tools like Jira, Trello, or Asana manage tasks, track progress, and collaborate in agile development environments.
Business Intelligence (BI) Tools
BI tools help analyze large datasets, create reports, and generate dashboards to provide stakeholders with actionable insights.
UML (Unified Modeling Language)
UML diagrams, including activity diagrams, class diagrams, and sequence diagrams, aid in visualizing system architecture and design.
Business analysts may use these techniques and tools based on the project’s complexity, the company’s preferences, and specific requirements. By leveraging these methodologies and technologies, business analysts can effectively analyze business processes, gather requirements, and provide valuable insights to drive successful IT projects.
When Do You Need Business Analysis?
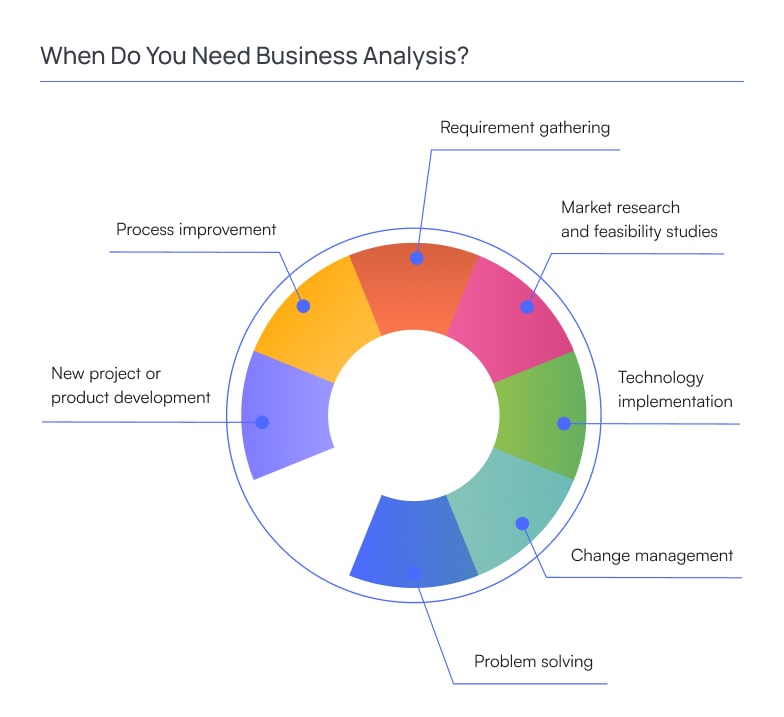
You need business analysis when you embark on a project or initiative involving any of the following situations:
New project or product development. When starting a new project or developing a new product, business analysis is essential to understand the project’s scope, gather requirements, and define the objectives. It ensures that the project aligns with the organization’s strategic goals and meets the needs of stakeholders and end-users.
Process improvement. If you are looking to optimize existing business processes, business analysis can help identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. Through analysis and data gathering, business analysts can recommend effective solutions to enhance efficiency and productivity.
Requirement gathering. Business analysis is crucial when gathering comprehensive and precise requirements for a software development project or any other initiative. BAs facilitate effective communication between stakeholders and the technical team, ensuring that all essential requirements are understood and documented accurately.
Market research and feasibility studies. Business analysis is valuable when conducting market research or feasibility studies for potential projects or new business ventures. It helps assess market demands, potential risks, and the viability of a project before committing resources.
Technology implementation. Before implementing new technologies or IT systems, business analysis is necessary to understand the impact on existing processes, identify integration requirements, and ensure that the technology aligns with business needs.
Change management. When significant organizational changes, such as mergers, acquisitions, or restructuring, business analysis can help assess the impact on business processes, define new requirements, and support the transition smoothly.
Problem solving. When facing complex business challenges or trying to address specific issues within an organization, business analysis provides a structured approach to analyze problems, identify root causes, and propose practical solutions.
In summary, business analysis is necessary to make informed and data-driven decisions, whether starting a new project, improving existing processes, implementing technology, or understanding user needs. By employing business analysis techniques, you can ensure that your projects are well-defined, aligned with business goals, and more likely to succeed.
Summing Up
The significance of business Analysis in driving successful projects cannot be overstated. As organizations navigate an increasingly complex business landscape, the role of a business analyst in software development becomes pivotal in bridging the gap between visionary goals and tangible outcomes. By meticulously gathering and analyzing requirements, identifying bottlenecks, and proposing innovative solutions, business analysts empower organizations to make informed decisions grounded in data and strategic insight.
As you can see in the article, business Analysts serve as facilitators, communicators, and problem-solvers, fostering collaboration between stakeholders and project teams. They ensure that projects align with business objectives, delivering products and solutions that meet end-users’ needs. Moreover, their skills in data analysis, domain knowledge, and effective communication establish them as catalysts for continuous improvement and efficiency gains within an organization.
As businesses strive to stay agile, customer-centric, and responsive to market demands, the role of business analysis will continue to evolve.
By leveraging the expertise of business analysts, companies can confidently navigate uncertainty, seize opportunities, and achieve remarkable success in a rapidly changing world.
Let our team of experienced business analysts be your assistants. Contact Binerals today to find out how we can streamline your processes and deliver results that exceed expectations.
Contact BineralsFAQ
What is business analysis in software development?
Business analysis is a discipline that involves identifying business needs, eliciting and analyzing requirements, and proposing solutions to achieve project goals. It plays a vital role in project management as it ensures projects are aligned with business objectives, mitigates risks, and delivers solutions that meet users’ needs effectively.What skills are essential for a proficient business analyst?
A proficient business analyst requires a diverse skill set, including strong analytical abilities, effective communication, problem-solving skills, domain knowledge, and data-gathering and modeling techniques. These skills enable them to excel in understanding business needs and delivering successful projects.How can we get started with business analysis in our organization?
To get started with business analysis, consider partnering with experienced business analysts that many software development companies have. Binerals is not an expectation, and we provide business analysis services.Or you can invest in training your existing team. Conduct a comprehensive analysis of your projects and processes to identify areas for improvement. Embrace data-driven decision-making and adopt the techniques and tools used in business analysis to optimize your projects for success.
